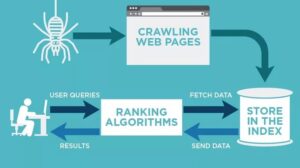
Most search engines build an index based on crawling, which is the process through which engines like Google, Yahoo and others find new pages to index. Mechanisms known as bots or spiders crawl the Web looking for new pages .
The bots typically start with a list of website URLs determined from previous crawls. When they detects new links on these pages, through tags like HREF and SRC, they add these to the list of sites to index.
Then, search engines use their algorithms to provide you with a ranked list from their index of what pages you should be most interested in based on the search terms you used.
Then, the engine will return a list of Web results ranked using its specific algorithm. On Google, other elements like personalized and universal results may also change your page ranking. In personalized results, the search engine utilizes additional information it knows about the user to return results that are directly catered to their interests.
Universal search results combine video, images and Google news to create a bigger picture result, which can mean greater competition from other websites for the same keywords.
Search engines have three primary functions:
- Crawl: Scour the Internet for content, looking over the code/content for each URL they find.
- Index: Store and organize the content found during the crawling process. Once a page is in the index, it’s in the running to be displayed as a result to relevant queries.
- Rank: Provide the pieces of content that will best answer a searcher’s query, which means that results are ordered by most relevant to least relevant.
How search engines make an index
To find what you’re after, a search engine will scan its index of webpages for content related to your search.
A search engine makes this index using a program called a ‘web crawler’. This automatically browses the web and stores information about the pages it visits.
Every time a web crawler visits a webpage, it makes a copy of it and adds its URL to an index. Once this is done, the web crawler follows all the links on the page, repeating the process of copying, indexing and then following the links. It keeps doing this, building up a huge index of many webpages as it goes.
Some websites stop web crawlers from visiting them. These pages will be left out of the index, along with pages that no-one links to.
The information that the web crawler puts together is then used by search engines. It becomes the search engine’s index. Every webpage recommended by a search engine has been visited by a web crawler.
What is search engine crawling?
Google Spiders (Bots) usually begin with heavily used servers and the most popular pages and from there, will index the words on each page. Next, they will follow each link that is found on the site.
This process allows the automated bots to place each page in an authoritative order and to place them in categories relevant to user searches.
Next, these spiders take note of all the words used and where these words are placed on a site.
Crawling is the discovery process in which search engines send out a team of robots (known as crawlers or spiders) to find new and updated content. Content can vary — it could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc. — but regardless of the format, content is discovered by links.
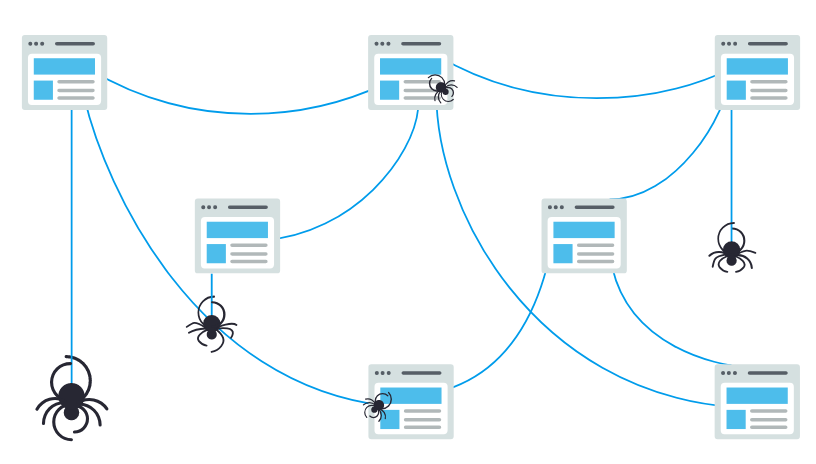
Googlebot starts out by fetching a few web pages, and then follows the links on those webpages to find new URLs. By hopping along this path of links, the crawler is able to find new content and add it to their index called Caffeine — a massive database of discovered URLs — to later be retrieved when a searcher is seeking information that the content on that URL is a good match for. This placement determines the relevance and importance of each word. These words can be contained in a link, header, title, list, or paragraph.
What is a search engine index?
Search engines process and store information they find in an index, a huge database of all the content they’ve discovered and deem good enough to serve up to searchers.
Search engine ranking
When someone performs a search, search engines scour their index for highly relevant content and then orders that content in the hopes of solving the searcher’s query. This ordering of search results by relevance is known as ranking. In general, you can assume that the higher a website is ranked, the more relevant the search engine believes that site is to the query.
It’s possible to block search engine crawlers from part or all of your site, or instruct search engines to avoid storing certain pages in their index. While there can be reasons for doing this, if you want your content found by searchers, you have to first make sure it’s accessible to crawlers and is indexable. Otherwise, it’s as good as invisible.
the engine will return a list of Web results ranked using its specific algorithm. On Google, other elements like personalized and universal results may also change your page ranking. In personalized results, the search engine utilizes additional information it knows about the user to return results that are directly catered to their interests. Universal search results combine video, images and Google news to create a bigger picture result, which can mean greater competition from other websites for the same keywords.
Here are the top elements to edit when designing your store for SEO:
Architecture – Make websites that search engines can crawl easily. This includes several elements, like how the content is organized and categorized and how individual websites link to one another. An XML sitemap can allow you to give a list of URLs to search engines for crawling and indexing. (2)
Content – Great content is one the most important elements for SEO because it tells search engines that your website is relevant. This goes beyond just keywords to writing engaging content your customers will be interested in on a frequent basis.
Links – When a lot of people link to a certain site, that alerts search engines that this particular website is an authority, which makes its rank increase. This includes links from social media sources. When your site links to other reputable platforms, search engines are more likely to rate your content as quality also.
Keywords– The keywords you use are one of the primary methods search engines use to rank you. Using carefully selected keywords can help the right customers find you. If you run a jewelry store but never mention the word “jewelry,” “necklace,” or “bracelet,” Google’s algorithm may not consider you an expert on the topic.
Title descriptions – While it may not show up on the website, search engines do pay attention to the title tag in your site’s html code, the words between < title > < /title >, because it likely describes what the website is about, like the title of a book or a newspaper headline.
Page content – Don’t bury important information inside Flash and media elements like video. Search engines can’t see images and video or crawl through content in Flash and Java plugins.
Internal links – Including internal links helps search engines crawl your website more effectively, but also boosts what many SEO professionals refer to as “link juice.” In other words, it has the same benefit of any link to your site: It demonstrates the value of your content.